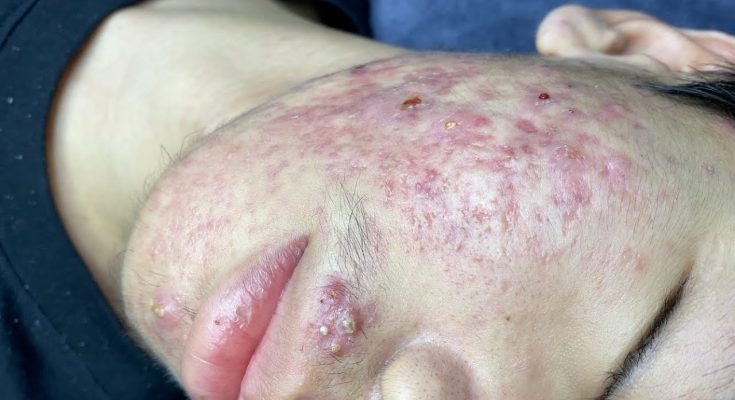
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can manifest in various forms, including whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, and cystic lesions. The image above shows a severe case of acne, which can be distressing for those affected. Understanding the causes and treatment options can help manage this condition effectively.
Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. Several factors can contribute to this, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones, especially androgens, increase during puberty and cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce more sebum. Hormonal changes related to pregnancy and the use of oral contraceptives can also affect sebum production.
- Genetics: A family history of acne can increase the likelihood of developing it.
- Certain Medications: Drugs containing corticosteroids, testosterone, or lithium can exacerbate acne.
- Diet: While the role of diet in acne is still debated, some studies suggest that certain foods, including carbohydrate-rich foods, dairy products, and chocolate, might trigger acne.
- Stress: Stress doesn’t cause acne but can make it worse.
Treatment Options
Treating acne often involves a combination of self-care and medical treatments:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter products containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or alpha hydroxy acids can help reduce acne. Prescription topical treatments may include retinoids, antibiotics, or stronger benzoyl peroxide formulations.
- Oral Medications: For more severe acne, doctors might prescribe oral antibiotics, hormonal treatments, or isotretinoin (a powerful drug reserved for severe cases).
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a regular skincare routine, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress can help control acne.
- Procedures: Dermatological procedures such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and extraction of whiteheads and blackheads can be beneficial.
Skincare Tips for Acne-Prone Skin
- Cleanse Gently: Use a mild cleanser twice daily to remove excess oil and dirt without irritating the skin.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Touching your face can transfer bacteria and oils from your hands to your skin, potentially worsening acne.
- Use Non-Comedogenic Products: opt for makeup, sunscreen, and moisturizers labeled as non-comedogenic, meaning they won’t clog pores.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep your skin hydrated and can reduce the likelihood of clogged pores.
Acne is a manageable condition with the right approach and treatment. If over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle changes don’t improve your acne, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options. Remember, while acne can be persistent, with patience and proper care, clearer skin is achievable.